Measuring air quality helps keep our environment healthy and safe for everyone, and one common tool for this is called the Normal Air Quality Index (AQI). The AQI gives a simple way to understand how clean or polluted the air is. But how accurate is it? Can professionals rely on it alone to measure air quality? Here, we’ll explore what the AQI does, how professionals use it, and its strengths and weaknesses.


What Is the Normal Air Quality Index?
The Normal Air Quality Index (AQI) is a tool that shows how clean or polluted the air is. The AQI scale goes from 0 to 500 and divides air quality into six levels:
- 0–50 (Good): Air quality is great, and everyone can go outside without worry.
- 51–100 (Moderate): Air is still okay, but some people might feel slight discomfort.
- 101–150 (Unhealthy for Sensitive Groups): People with asthma, young children, and old age people might feel affected.
- 151–200 (Unhealthy): The air can cause health problems for everyone, especially if they go outside.
- 201–300 (Very Unhealthy): Serious health warnings and everyone should avoid outdoor activities.
- 301–500 (Hazardous): The air is very dangerous; people should stay indoors.
The AQI measures five main pollutants:
- Ozone near the ground
- Small particles in the air (PM10 and PM2.5)
- Carbon monoxide
- Sulfur dioxide
- Nitrogen dioxide
AQI updates daily, sometimes even hourly, helping people understand whether spending time outside is safe. For a detailed insight into how air quality affects people and what symptoms they experience, read the article Symptoms of Breathing Poor Air Quality.
How Do Professionals Use the Normal Air Quality Index?
- Checking Daily Air Quality Levels
Organizations use AQI readings from sensors all over a city to check if the air quality is good or needs caution. By using these AQI numbers, they can alert people if pollution levels are high.
2. Issuing Health Warnings
If AQI levels are “Unhealthy” or higher, warnings are issued to protect people’s health, especially those sensitive to pollution, such as young children, elderly people, and those with breathing issues.
3. Tracking Pollution Patterns
Professionals can see trends by looking at AQI readings over time. For example, air quality might get worse in certain seasons. These trends help cities make decisions about laws to control pollution.
4. Setting Rules to Keep Air Clean
AQI data can help the government decide if new laws are needed, such as reducing car emissions or stopping certain factory pollutants.

Limitations
While the AQI is helpful, it doesn’t tell us everything about air quality. Here are some limitations:
- Measures Only a Few Pollutants
The AQI focuses on just five pollutants, even though there are other harmful chemicals in the air, like gases from factories or paints. So, AQI might miss some pollution in certain areas, like near chemical plants.
2. Basic Health Advice
AQI provides general advice, but even low or moderate levels of pollution might still affect some people with health problems. Doctors and health experts may provide additional guidance beyond the AQI.
3. Not Everywhere
AQI sensors are mainly in cities, so getting precise AQI data for rural or remote areas is hard. Often, professionals will estimate AQI in areas with fewer sensors, which may not be very accurate.
4. Changing Weather Conditions
Weather affects air quality. For example, windy days might lower pollution, while sunny days can increase ground-level ozone. Since weather changes quickly, AQI numbers can go up or down in a short time.
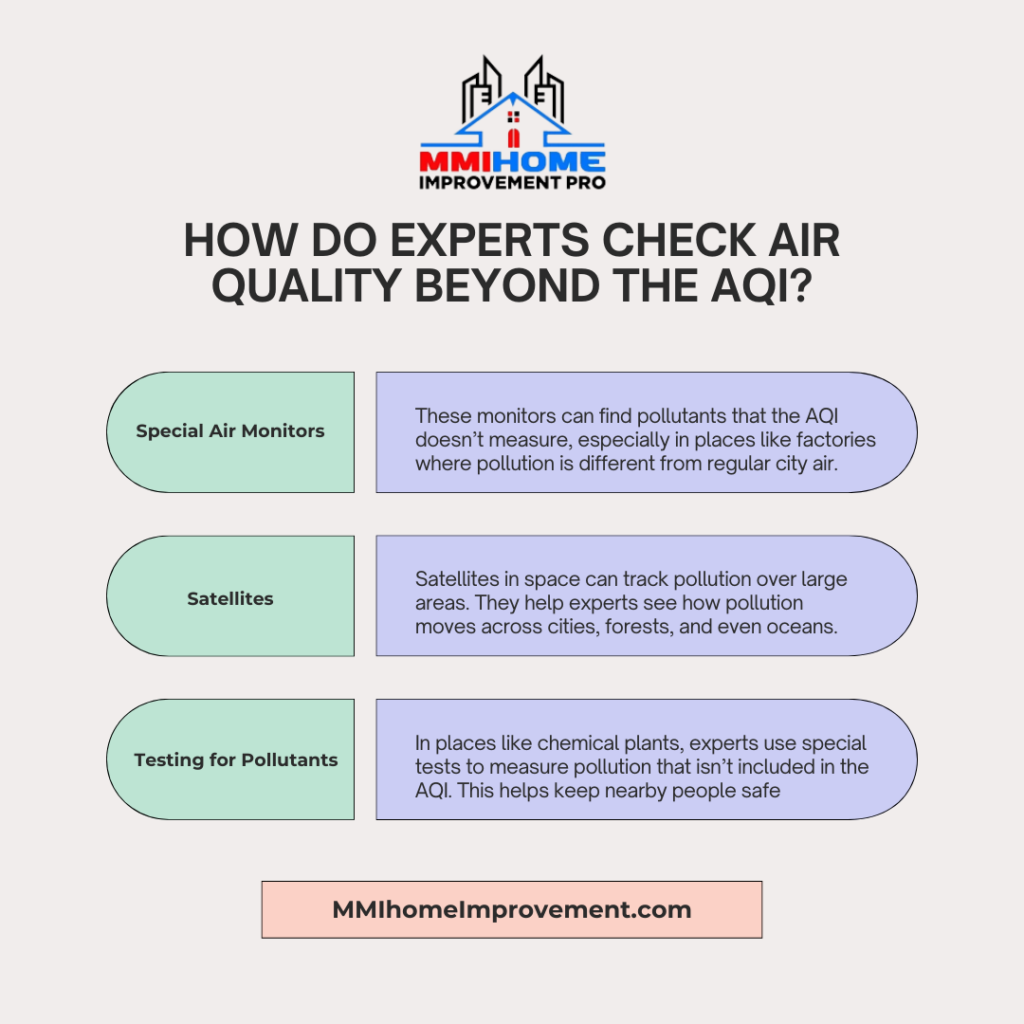
How Do Experts Check Air Quality Beyond the AQI?
The Air Quality Index (AQI) is helpful, but sometimes, experts need more information to understand air quality fully. Here are some tools they use:
- Special Air Monitors
These monitors check for more pollutants than the AQI measures. They can detect other harmful chemicals in the air that the AQI doesn’t cover. This is important near factories or places where pollution differs from regular city air.
2. Satellites in Space
Satellites can track air pollution from space, which is helpful in areas without monitors on the ground. Satellites show large areas and help experts see how pollution moves across cities, forests, and oceans.
3. Extra Testing for Different Pollutants
Some places, like chemical plants, create specific types of pollution that aren’t in the AQI. Experts use special tests to measure these unique pollutants. This helps people nearby stay safe by knowing exactly what’s in the air.
Experts use these tools along with the AQI to get a clearer picture of air quality. This way, they can keep communities safer by understanding precisely what pollutants are around, especially in places where AQI data might not tell the whole story.
Use the below code to embed this infographic
Is the Normal Air Quality Index Reliable?
For most people, the Normal Air Quality Index works well as a guide for deciding whether going outside is safe. It’s easy to understand and provides useful information for daily decisions. However, some people, especially those with health issues, may need more detailed air quality information. In those cases, professionals often provide extra guidance.
Summary
The Normal Air Quality Index is very helpful for professionals and the public. It gives a quick view of air quality, helping people know if going outside is safe. Professionals use it to track pollution patterns, set rules, and protect public health. While it has limitations, the AQI is a reliable tool, mainly when used with other methods to make sure everyone stays safe and healthy.

